Key Points of Pre-treatment Quality Control
- Multi-batch, small-batch parallel production
- Frequent urgent orders and special orders
- Similar part specifications with high risks of mixed materials
- Clear traceability of quality responsibility is required
In this context, pre-treatment is not just about “cleaning the parts,” but rather about building a systematic quality foundation.
Based on years of coating processing experience, Junhe, while retaining mature and rigorous pre-treatment quality control requirements, has introduced digitalized coating equipment and process management logic. This allows processes that were once highly dependent on human intervention to gradually transform into standardized procedures that are controllable, traceable, and reusable.
B. Loading capacity, conveyor belt speed, and degreasing temperature (note the heat treatment temperature of the blank and the size, shape, and thickness of the parts);
C. Prevent mixing, collision, or damage of parts during loading;
D. Loading and unloading methods (manual or automatic);
E. Necessary anti-collision measures, such as baffles and reducing the drop height;
F. Self-inspection by employees after degreasing—water film method;
G. Timely filling out actual process parameters (loading capacity, baking temperature, conveyor belt speed), and self-inspection records;
H. First inspection, in-process inspection, and last inspection parts must be sampled.
- Some parts that are unsuitable for high-temperature degreasing: parts that deform after high temperature, parts with rubber gaskets, elastic components, metal thin sheets, electroplated undercoats, or aluminum/zinc alloy castings;
- Eliminate iron shovel transfers; be cautious of missing blanks in incoming material packaging; ensure operators compare similar parts, and whether the shift leader has arranged for these parts to be degreased separately (or use separation tools), and manually fill in the process identification card.
02 Key Points for High-Temperature Degreasing Operations
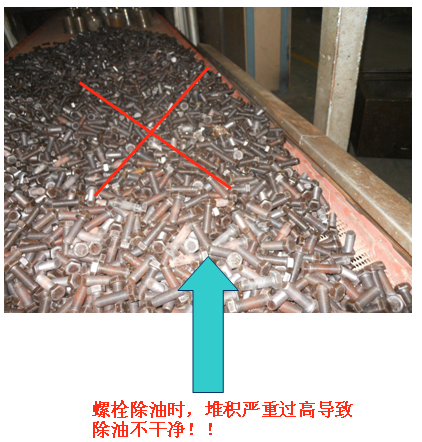
- During loading, parts must be differentiated to prevent mixing.
- Try to gently place parts on the conveyor belt, especially to avoid directly throwing degreased parts onto the belt, which could damage the surface (e.g., threads).
- For bolts larger than M20 (including M20) or large parts, manual loading is required.
- For large parts (such as wind turbine bolts, shafts, etc.), leave a gap between parts when loading to prevent incomplete or inadequate degreasing.
- After degreasing, check if the containers for parts are clean before loading.
- Ensure the appropriate loading capacity/volume.
- Make sure the carts are placed in designated areas and are arranged neatly.
- For similar parts, take effective measures to prevent mixing (e.g., using different colored cards to distinguish them).



The specific operation method is to wash the degreased part with water, then place it vertically for 30 seconds. If the water film on the surface of the part splits, it indicates that the degreasing was not clean, and the part needs to be degreased again.
C. Record the inspection results as required.
Note: If employees/inspectors find any anomalies, they should provide feedback to the shift leader. The inspector will issue a “Quality Abnormality Handling Form” according to the regulations and track the implementation of corrective actions.
Solvent Degreasing
01 Quality Control Requirements
a. Degreasing temperature, loading capacity, cleaning time
b. Regularly clean or replace the tank solution as required
c. Proper loading/unloading of parts (specified vehicles and capacity), product placement, and mixing control
d. Physical quality inspection of the products
02 Self-Inspection
A. Check for thread damage after degreasing—visual inspection or use the corresponding go/no-go gauge.
 B. Degreasing Effect Inspection – Water Film Method;
B. Degreasing Effect Inspection – Water Film Method;
The specific procedure is to wash the degreased part with water, then place it vertically for 30 seconds. If there is any splitting of the water film on the surface of the part, it indicates that the degreasing was not thorough, and the part needs to be degreased again.
C. Record the inspection results as required.
Note: If employees/inspectors find any anomalies, they should provide feedback to the shift leader. The inspector will issue a “Quality Abnormality Handling Form” as per the regulations and track the implementation of corrective actions.
03 Causes of Poor Degreasing Effect
- Improper selection of cleaning solvents;
- Cleaning time too short;
- Low evaporation temperature;
- Excessive loading capacity;
- High oil content in the working solution;
- Incoming materials are too oily.
Shot Blasting for Rust Removal
01 Quality Control Requirements
A. Before shot blasting, check if the shot blasting equipment is properly started, if equipment inspections are complete, and if steel shots and other non-batch parts scattered around the equipment have been cleaned up.
B. Verify the process identification card and process sheet (production will be rejected without a process sheet);
C. Set the loading capacity, time, current, steel shot specifications/proportions, blasting head frequency, track frequency, machine number, etc., according to the process sheet requirements;
D. Strictly prohibit unauthorized changes from “hanging blast” to “rolling blast” when the process is defined as hanging blast;
E. After shot blasting, if the parts have dust or steel shots on them, extend the idle time to remove them;
F. The rotation speed of the track during rolling blast (especially important for parts like Dexing brake discs, Hongguang slot-shaped seats, etc.);
G. Pay attention to whether the parts after the first frame shot blasting have any damage or deformation, and make adjustments accordingly;
H. Ensure the use of correct tooling and fixtures (including for Dexing brake discs);
I. For manual loading/unloading of parts according to shot blasting operating procedures:
| Coarse-thread bolts | Specifications ≥ M20180, ≥ M24150, M27 and above |
| Fine-pitch bolt | ≥ M16×120, ≥ M18×150, ≥ M20×120, M24 and above |
| Fittings | Large accessories weighing more than 2kg |
| Parts with special requirements | For example, 03091 and 07002 will be indicated on the process sheet |
Shot Blasting Operation Points
- Before loading, check if the storage trolleys/containers have been cleaned.
- Ensure the loading capacity/volume is appropriate.
- Ensure trolleys are placed in the designated area and arranged neatly.
- Ensure effective measures are taken to prevent confusion between similar parts (e.g., using color cards for differentiation).
- Transfer parts to the designated area promptly after shot blasting, or implement measures to prevent secondary contamination.
- Coating should generally be applied within 8 hours after shot blasting, or within 2 hours under high temperature and high humidity conditions.
Self-Inspection Methods
B. Check for any collision damage after shot blasting.
C. Physical surface inspection: Check for surface oxide scale, dust, and oil residue.
■ Use a flashlight to inspect the bottom of the threads for fine-pitch bolts.
■ Any remaining traces should only be slight spot-like or streaky discoloration left from the raw material heat treatment process.
■ Testing can be performed using 3M tape or the copper sulfate method (optimal method).
D. Rust Removal Effectiveness Check
■Inspect carefully with the naked eye. The workpiece surface must be free of rust spots, oxide scale, and dirt. It should achieve the standard of “complete removal of rust and oxide scale, with a dust-free surface
■ After shot blasting, the workpiece must be wiped with a clean cloth or paper to check for any adhering rust, iron filings, or dust.
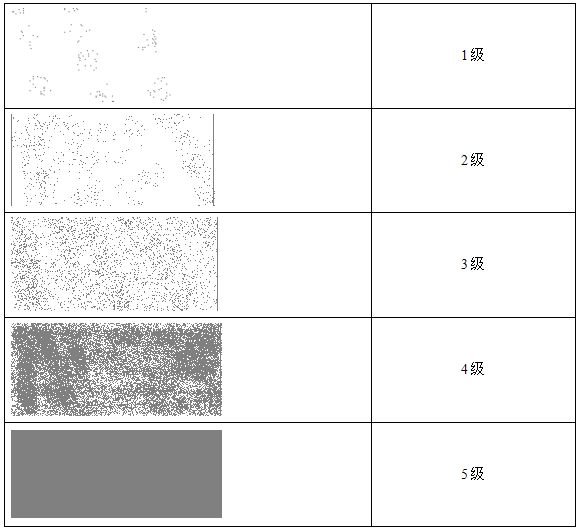
■Perform a 3M tape test. Check for heavy dust/iron filings adhesion. Standard: Grade ≥ 3.
■The copper sulfate method may also be used if necessary
Key Focus Areas
- Check for thread damage: (Shot blasting poses the highest risk of causing damage or deformation to parts).
- Check for deformation of elastic components.
- Check for edge curling on part corners: (Specifically for connecting rods).
- Check for trapped steel shots: (Common in nuts, washer-faced bolts/nuts, and coarse threads).
- Check for mixed materials.
- Weekly inspection of shot blasting media: (Check shot size ratio, oil/water contamination, additions or replacements, shot specifications/hardness, and maintain corresponding records).
- Post-shift equipment cleaning: (Check if employees cleaned the equipment at the end of their shift).
Measures to Improve Shot Blasting Effectiveness
- Extend the shot blasting time.
- Add or replace the shot media (adjust quantity/specifications) and increase the shot blasting current.
- Reduce the loading capacity.
- Switch to a different shot blasting machine.
- Adjust the track rotation speed.
Post time: Jan-19-2026